Description:
I know many novice android programmer are facing problem to implement multi-column listview or in confusion to implement this kind of view. so let me write here to implement multi columnr listview by using ListView itself.
Yes, its little bit tricky but if you have gone through my previous articles for creating Custom ListView then you will sure realize that its just a difference of creating listView_row xml layout file. Just go through the above link.
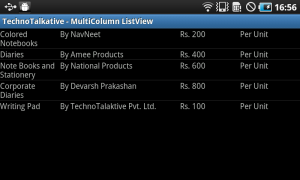
Output:
Solution:
I haven’t done any magic but created a listview_row.xml as:
And now you can define the custom adapter for this listview same as our practice of defining custom adapter for ListView.
listview_row.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout
android:id="@+id/relativeLayout1"
android:layout_height="fill_parent"
android:layout_width="fill_parent"
xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android">
<TextView
android:id="@+id/FirstText"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="First"
android:layout_weight="1">
</TextView>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/SecondText"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Second"
android:layout_weight="2">
</TextView>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/ThirdText"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Third"
android:layout_weight="1">
</TextView>
<TextView
android:id="@+id/FourthText"
android:layout_width="0dp"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:text="Fourth"
android:layout_weight="1">
</TextView>
</LinearLayout>
main.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?>
<LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android"
android:layout_width="match_parent"
android:layout_height="match_parent"
android:orientation="vertical" >
<ListView
android:id="@+id/listview"
android:layout_height="wrap_content"
android:layout_width="match_parent">
</ListView>
</LinearLayout>
listviewAdapter.java
package com.paresh.demoexample;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.FIRST_COLUMN;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.SECOND_COLUMN;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.THIRD_COLUMN;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.FOURTH_COLUMN;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.view.LayoutInflater;
import android.view.View;
import android.view.ViewGroup;
import android.widget.BaseAdapter;
import android.widget.TextView;
/**
*
* @author Paresh N. Mayani
*/
public class listviewAdapter extends BaseAdapter
{
public ArrayList<HashMap> list;
Activity activity;
public listviewAdapter(Activity activity, ArrayList<HashMap> list) {
super();
this.activity = activity;
this.list = list;
}
@Override
public int getCount() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return list.size();
}
@Override
public Object getItem(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return list.get(position);
}
@Override
public long getItemId(int position) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return 0;
}
private class ViewHolder {
TextView txtFirst;
TextView txtSecond;
TextView txtThird;
TextView txtFourth;
}
@Override
public View getView(int position, View convertView, ViewGroup parent) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
ViewHolder holder;
LayoutInflater inflater = activity.getLayoutInflater();
if (convertView == null)
{
convertView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.listview_row, null);
holder = new ViewHolder();
holder.txtFirst = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.FirstText);
holder.txtSecond = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.SecondText);
holder.txtThird = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.ThirdText);
holder.txtFourth = (TextView) convertView.findViewById(R.id.FourthText);
convertView.setTag(holder);
}
else
{
holder = (ViewHolder) convertView.getTag();
}
HashMap map = list.get(position);
holder.txtFirst.setText(map.get(FIRST_COLUMN));
holder.txtSecond.setText(map.get(SECOND_COLUMN));
holder.txtThird.setText(map.get(THIRD_COLUMN));
holder.txtFourth.setText(map.get(FOURTH_COLUMN));
return convertView;
}
}
MultiColumnActivity.java
package com.paresh.demoexample;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.FIRST_COLUMN;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.SECOND_COLUMN;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.THIRD_COLUMN;
import static com.paresh.demoexample.Constant.FOURTH_COLUMN;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.HashMap;
import android.app.Activity;
import android.os.Bundle;
import android.widget.ListView;
/**
*
* @author Paresh N. Mayani
*/
public class MultiColumnActivity extends Activity
{
private ArrayList<HashMap> list;
public void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState)
{
super.onCreate(savedInstanceState);
setContentView(R.layout.main);
ListView lview = (ListView) findViewById(R.id.listview);
populateList();
listviewAdapter adapter = new listviewAdapter(this, list);
lview.setAdapter(adapter);
}
private void populateList() {
list = new ArrayList<HashMap>();
HashMap temp = new HashMap();
temp.put(FIRST_COLUMN,"Colored Notebooks");
temp.put(SECOND_COLUMN, "By NavNeet");
temp.put(THIRD_COLUMN, "Rs. 200");
temp.put(FOURTH_COLUMN, "Per Unit");
list.add(temp);
HashMap temp1 = new HashMap();
temp1.put(FIRST_COLUMN,"Diaries");
temp1.put(SECOND_COLUMN, "By Amee Products");
temp1.put(THIRD_COLUMN, "Rs. 400");
temp1.put(FOURTH_COLUMN, "Per Unit");
list.add(temp1);
HashMap temp2 = new HashMap();
temp2.put(FIRST_COLUMN,"Note Books and Stationery");
temp2.put(SECOND_COLUMN, "By National Products");
temp2.put(THIRD_COLUMN, "Rs. 600");
temp2.put(FOURTH_COLUMN, "Per Unit");
list.add(temp2);
HashMap temp3 = new HashMap();
temp3.put(FIRST_COLUMN,"Corporate Diaries");
temp3.put(SECOND_COLUMN, "By Devarsh Prakashan");
temp3.put(THIRD_COLUMN, "Rs. 800");
temp3.put(FOURTH_COLUMN, "Per Unit");
list.add(temp3);
HashMap temp4 = new HashMap();
temp4.put(FIRST_COLUMN,"Writing Pad");
temp4.put(SECOND_COLUMN, "By TechnoTalaktive Pvt. Ltd.");
temp4.put(THIRD_COLUMN, "Rs. 100");
temp4.put(FOURTH_COLUMN, "Per Unit");
list.add(temp4);
}
}
Constant.java
package com.paresh.demoexample;
/**
*
* @author Paresh N. Mayani
*/
public class Constant {
public static final String FIRST_COLUMN = "First";
public static final String SECOND_COLUMN = "Second";
public static final String THIRD_COLUMN = "Third";
public static final String FOURTH_COLUMN = "Fourth";
}
Download full Example from Here: Android – Multi Column ListView
Please feel free to give comment/feedback if you are knowing better solutions than this. 🙂